Professor Prokofiev's Group: Current Projects
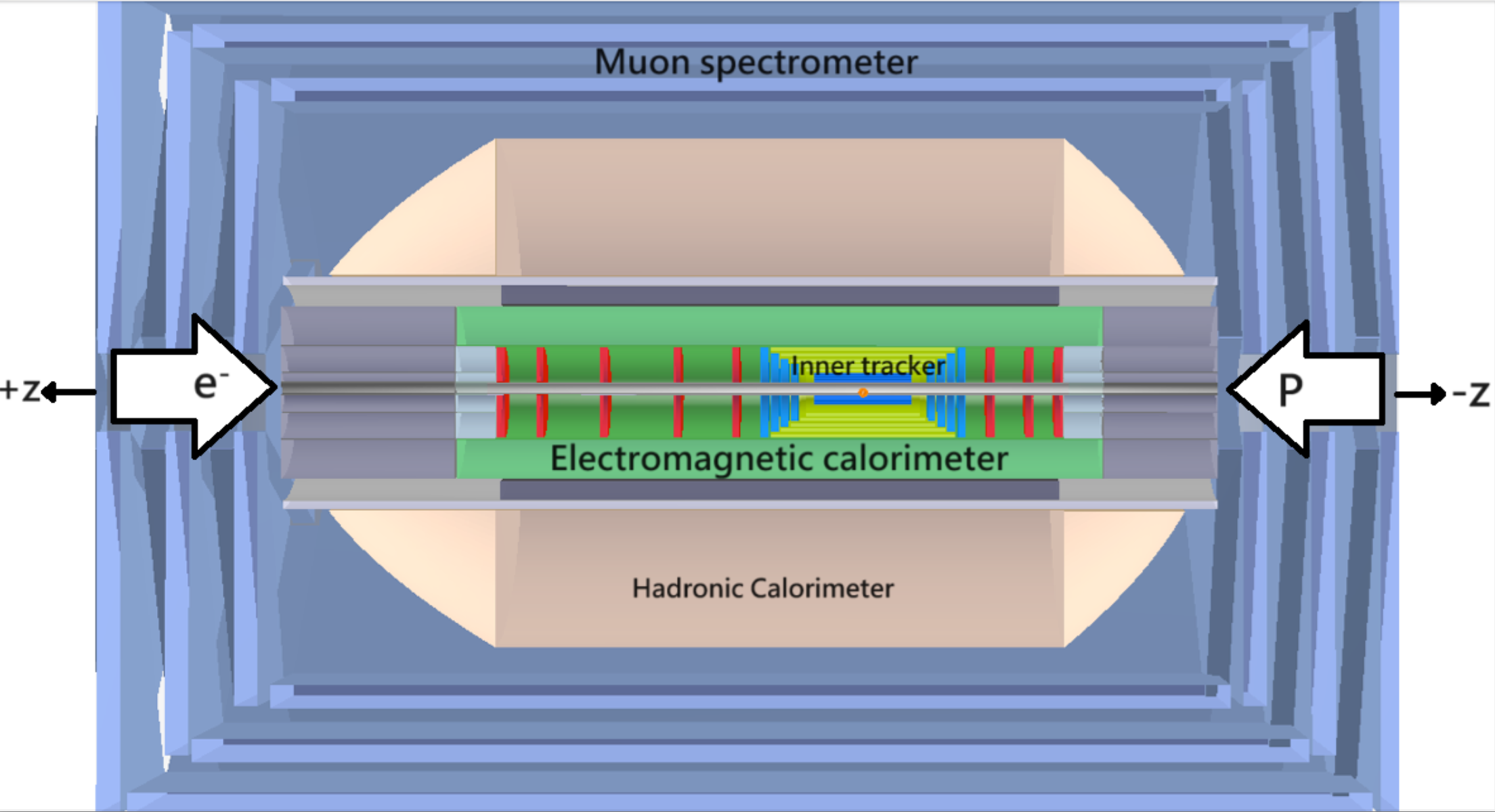
Higgs Physics with the ATLAS Detector
Since the discovery of the Higgs boson in 2012, our group is actively involved in studies of its properties. Our current focus is on the tensor structure of the Higgs boson couplings to other Standard Model particles. By comparing the measured properties to the corresponding theory expectations, we hope to find tiny deviations from the Standard Model predictions, which may shed light on mysterious new physics beyond the Standard Model. The Higgs decay channels we are currently most active in are: H->ZZ->4l and H->tau tau.

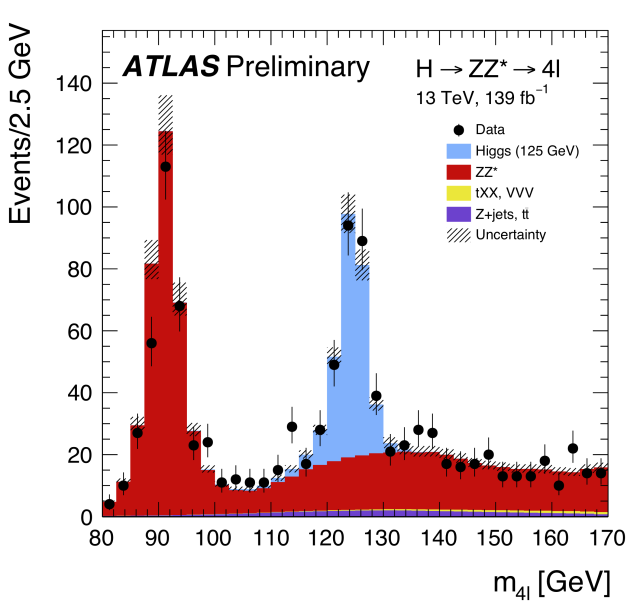
Distribution of the invariant mass of the four leptons selected in the ATLAS measurement of H→ZZ*→4ℓ using the full Run 2 dataset. The Higgs boson corresponds to the excess of events (blue) over the non-resonant ZZ* background (red) at 125 GeV. A peak around Z boson mass at 91 GeV can be observed, composed of the ZZ* background events.(Image: ATLAS Collaboration/CERN)
Unified Graph Neural Network for Tau Identification and Decay Mode Classification
In the ATLAS experiment at CERN, various methods are employed for Tau identification (TauID) and decay mode (DM) classification. The current TauID method is GNTau, a graph neural network (GNN)-based approach derived from the GN2 model developed by the Flavour Tagging group. For DM classification, the DeepSet neural network is used, which was introduced around 2020.
Given the proven efficacy of GNN-based models in TauID and flavour tagging, a new GNN-based DM classification model is being considered. Moreover, since the same architecture could serve both TauID and DM classification, a unified model for these tasks is also under exploration.
The primary objective of this project is to develop such a unified model, which is anticipated to lower maintenance costs for Tau analysis and potentially improve performance in both TauID and DM classification.
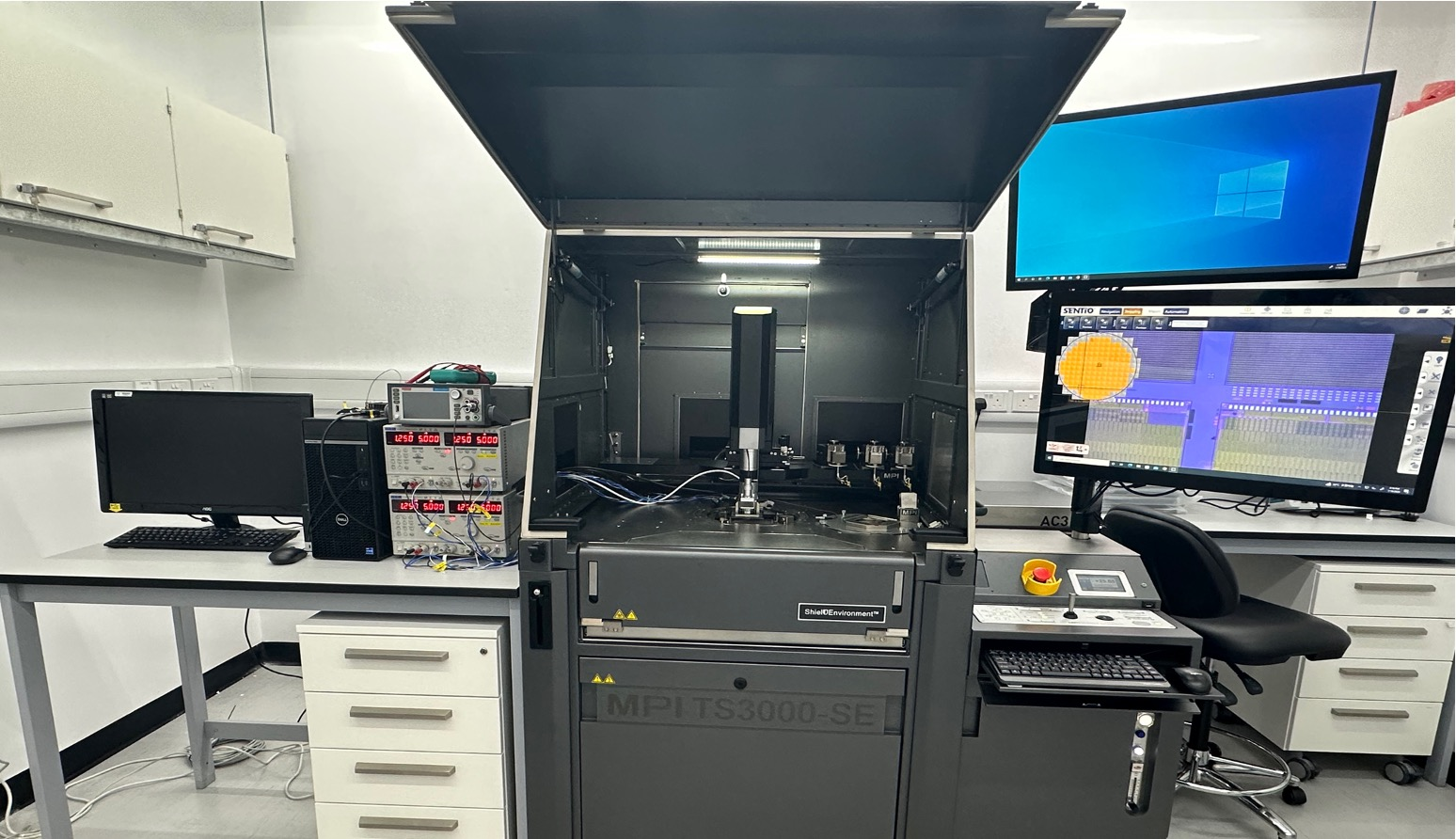
ATLAS Inner Tracker Upgrade
The unprecedented particle rates at the High-Luminosity LHC demand a new generation of radiation-hard and high-precision silicon sensors. Our team in Hong Kong is contributing to this upgrade by performing quality control for the ATLAS ITk Pixel Detector. Using a probe station, we conduct electrical testing of pixel sensor batches, characterising each chip to ensure it meets performance standards.This process identifies and maps functional sensors, allowing only certified modules to be selected for assembly into the final detector barrels. This critical pre-installation screening ensures the reliability and precision required for the high-luminosity phase in 2029.

Higgs Physics at Future Accelerators
In preparation for the post-LHC era, our team is actively involved in investigating physics potential of planned future accelerators. Our focus is currently on the LHeC and CEPC initiatives.